So you’ve heard about occupational therapy, but did you know that it can also involve effective behavioral interventions? In this article, we’ll explore how occupational therapy can be used as a powerful tool to address behavioral challenges and improve overall well-being. From children with autism to adults with mental health disorders, occupational therapists are utilizing a range of strategies to promote positive behaviors and enhance daily functioning. Discover the key principles behind these interventions and see how occupational therapy is making a meaningful impact in the lives of individuals across various age groups and conditions.
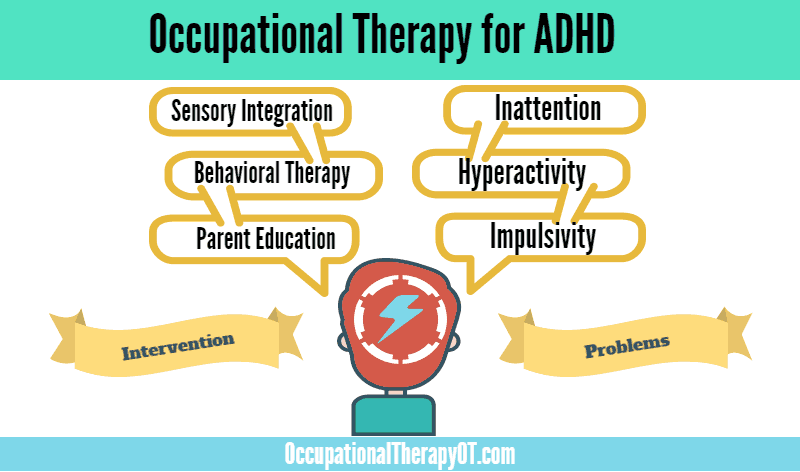
Definition of Occupational Therapy Behavioral Interventions
Explanation of occupational therapy
Occupational therapy is a healthcare profession that focuses on enabling individuals to participate in meaningful activities or occupations. The goal of occupational therapy is to promote health and well-being by addressing physical, mental, and emotional challenges that may limit a person’s ability to engage in daily activities. Occupational therapists use a holistic approach, taking into consideration the person’s environment and individual needs, to provide personalized interventions that support their overall function and independence.
Overview of behavioral interventions
Behavioral interventions in occupational therapy refer to the strategies and techniques used to address specific behavioral issues or challenges that individuals may face. These interventions aim to modify actions, thoughts, or environmental factors that may impact a person’s ability to participate in daily activities. By targeting behaviors and their underlying causes, occupational therapy behavioral interventions can help individuals develop functional and adaptive behaviors, thereby enhancing their overall well-being and quality of life.
Definition of occupational therapy behavioral interventions
Occupational therapy behavioral interventions are the specific interventions used by occupational therapists to address behavioral issues and challenges faced by individuals. These interventions are designed to promote positive changes in behavior through a variety of strategies, including positive and negative reinforcement, task modification, environmental adaptation, and cognitive-behavioral therapy. By implementing these interventions, occupational therapists can support individuals in developing and maintaining functional behaviors that enable them to engage in meaningful occupations.
Importance and Benefits of Occupational Therapy Behavioral Interventions
Improved quality of life
One of the key benefits of occupational therapy behavioral interventions is the improvement in an individual’s overall quality of life. By addressing behavioral issues that may be limiting participation in daily activities, occupational therapists can help individuals regain control over their lives and achieve a greater sense of routine, purpose, and satisfaction. Improved behavioral patterns foster a sense of accomplishment and empowerment, leading to increased overall well-being and a more meaningful life experience.
Increased independence and productivity
Occupational therapy behavioral interventions also play a crucial role in promoting independence and productivity. By targeting specific behaviors that may be hindering an individual’s ability to perform essential tasks, occupational therapists can help individuals acquire and refine the skills necessary for independent daily living. Through interventions such as task modification and cognitive-behavioral therapy, individuals can learn strategies to overcome challenges, leading to increased autonomy, efficiency, and productivity in their everyday lives.
Enhanced physical and mental well-being
Behavioral issues can have a significant impact on an individual’s physical and mental health. Occupational therapy behavioral interventions are designed to address these issues and promote overall well-being. Interventions such as positive reinforcement and environmental adaptation can help individuals establish and maintain healthy lifestyle habits, improve physical mobility, and manage chronic conditions effectively. Additionally, by targeting cognitive impairments and mental health conditions, occupational therapists can assist individuals in developing coping mechanisms, reducing symptoms, and improving emotional and psychological well-being.
Common Behavioral Issues Addressed in Occupational Therapy
Physical disabilities
Occupational therapy is often sought by individuals with physical disabilities that impact their ability to engage in daily activities. Behavioral issues related to physical disabilities can include difficulties with mobility, coordination, and self-care tasks. Occupational therapists employ a range of behavioral interventions, such as task modification and environmental adaptation, to address these challenges and enhance functional independence.
Cognitive impairments
Cognitive impairments, such as memory loss or difficulties with problem-solving, can significantly impact a person’s ability to perform daily tasks. Occupational therapy behavioral interventions focus on providing individuals with strategies and support to improve cognitive functioning. Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and task modification can help individuals with cognitive impairments regain and enhance their cognitive abilities, resulting in increased independence and improved daily functioning.
Mental health conditions
Occupational therapy is also instrumental in addressing behavioral issues associated with mental health conditions. Individuals experiencing mental health challenges may struggle with managing emotions, maintaining routines, or engaging in meaningful activities. Occupational therapists utilize a variety of behavioral interventions, including cognitive-behavioral therapy and positive reinforcement, to help individuals develop coping skills, establish effective routines, and reclaim control over their lives.
Neurological conditions
Neurological conditions, such as stroke or traumatic brain injury, can lead to behavioral challenges that impact an individual’s occupational performance. Occupational therapy behavioral interventions aim to address these challenges by targeting specific behaviors and underlying neurological impairments. Through the use of interventions like task modification and environmental adaptation, occupational therapists can help individuals regain lost skills, adapt to new challenges, and optimize their overall function.
Types of Behavioral Interventions Used in Occupational Therapy
Positive reinforcement
Positive reinforcement is a widely used behavioral intervention in occupational therapy. It involves rewarding desired behaviors to motivate individuals and facilitate their engagement in meaningful activities. By providing positive feedback, incentives, or rewards, occupational therapists encourage individuals to repeat and sustain functional behaviors, leading to increased independence and participation in daily activities.
Negative reinforcement
Negative reinforcement is another behavioral intervention employed in occupational therapy. It involves removing or avoiding unpleasant stimuli or consequences to encourage the desired behavior. By eliminating or reducing undesirable outcomes, occupational therapists reinforce functional behaviors and motivate individuals to engage in activities without the fear of negative consequences.
Task modification
Task modification is a behavioral intervention that focuses on adapting or simplifying activities or tasks to better match an individual’s abilities. Occupational therapists analyze the demands of specific tasks and make modifications to the environment, materials, or procedures to enhance a person’s success and promote independence. Task modification can involve breaking down complex tasks into smaller steps, providing assistive devices, or adjusting the physical environment to accommodate individual needs.
Environmental adaptation
Environmental adaptation is a key behavioral intervention in occupational therapy that involves modifying the physical environment to support a person’s occupational performance. Occupational therapists analyze the surroundings and make changes to enhance safety, accessibility, and usability. Examples of environmental adaptations include installing grab bars in bathrooms, rearranging furniture for optimal mobility, or implementing sensory-friendly environments for individuals with sensory processing challenges.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a widely used intervention in occupational therapy to address behavioral issues linked to cognitive impairments, mental health conditions, or neurological disorders. CBT focuses on identifying and changing unhelpful thoughts, beliefs, and behaviors that may contribute to difficulties in daily functioning. Occupational therapists use CBT techniques to help individuals recognize negative patterns, develop coping strategies, challenge irrational thoughts, and replace maladaptive behaviors with more functional alternatives.
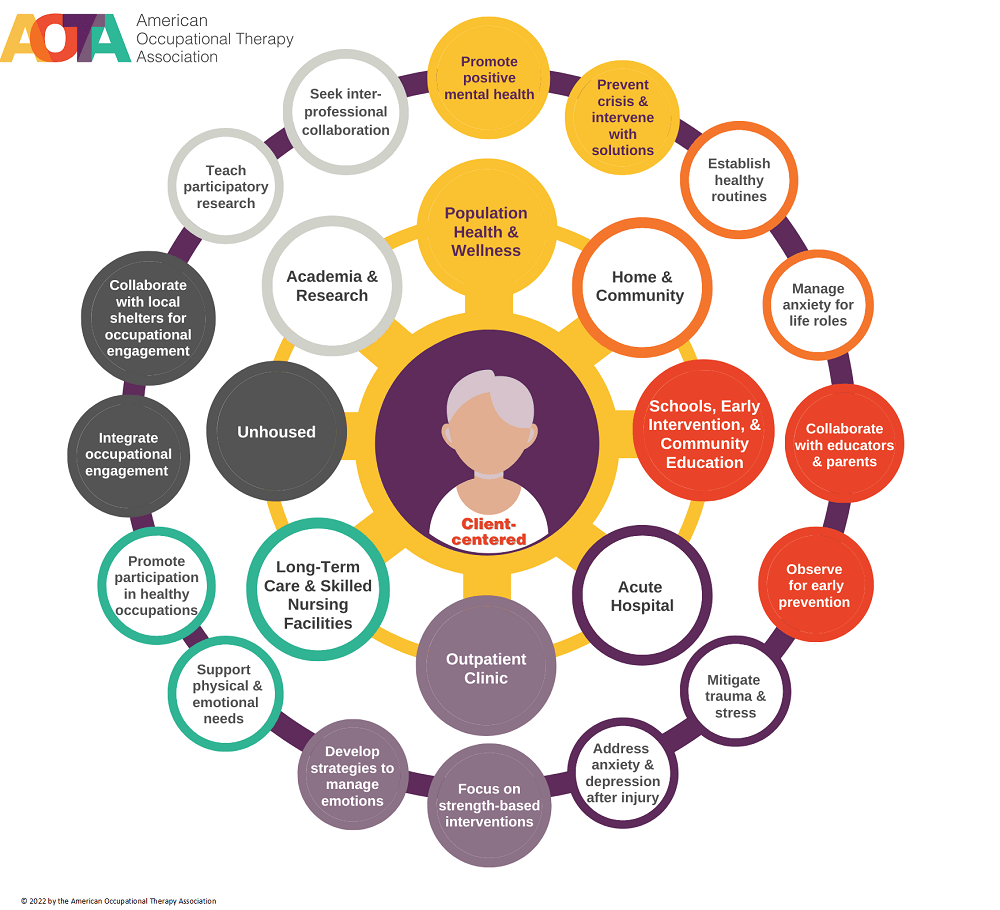
Goal Setting and Individualized Care Plans in Occupational Therapy Behavioral Interventions
Collaborative goal setting
In occupational therapy behavioral interventions, goal setting is a collaborative process between the occupational therapist and the individual receiving therapy. By working together, both parties identify the individual’s priorities, desired outcomes, and areas for improvement. Collaborative goal setting ensures that interventions align with the individual’s needs, values, and abilities, fostering a sense of ownership and motivation throughout the therapeutic process.
Person-centered care
Person-centered care is a fundamental aspect of occupational therapy behavioral interventions. It emphasizes the importance of tailoring interventions to meet the unique needs, preferences, and values of the individual. Occupational therapists consider the person’s cultural background, beliefs, and personal goals in order to create individualized care plans that promote meaningful and fulfilling engagement in daily activities.
Tailored interventions based on individual needs
In occupational therapy behavioral interventions, interventions are tailored to meet the individual’s specific needs and goals. Occupational therapists conduct thorough assessments to identify the underlying causes of behavioral issues and to better understand the person’s strengths, limitations, and environmental context. Based on this assessment, interventions are customized to address the individual’s unique challenges and to optimize their success in achieving their desired outcomes.
Assessment and Evaluation Process in Occupational Therapy Behavioral Interventions
Initial assessment
The initial assessment is a crucial step in occupational therapy behavioral interventions. It involves gathering information about the individual’s medical history, functional abilities, and specific behavioral issues. Occupational therapists use standardized assessments, interviews, and observations to gain a comprehensive understanding of the individual and their occupational performance. The initial assessment helps identify specific goals, prioritize interventions, and establish baseline measures for ongoing evaluation.
Ongoing evaluation
Ongoing evaluation is a continuous process in occupational therapy behavioral interventions. It involves monitoring the individual’s progress, reassessing goals, and adjusting interventions as needed. Occupational therapists use a range of evaluation techniques, including interviews, observations, and outcome measures, to assess changes in behavior, functional abilities, and overall well-being. Ongoing evaluation ensures that interventions remain effective and relevant, allowing for modifications or adaptations to optimize outcomes.
Outcome measurement
Outcome measurement is an essential component of occupational therapy behavioral interventions. It involves assessing and documenting the changes in an individual’s behavior, functional abilities, and overall well-being as a result of the interventions. Occupational therapists utilize standardized outcome measures, self-report measures, and objective observations to quantify the impact of interventions and inform future treatment planning. Outcome measurement allows therapists to track progress and demonstrate the effectiveness of behavioral interventions to the individual, their caregivers, and other healthcare professionals.
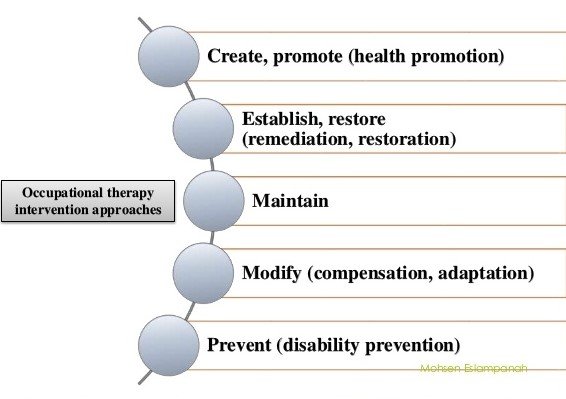
Evidence-Based Practice in Occupational Therapy Behavioral Interventions
Research studies supporting the effectiveness of behavioral interventions
Occupational therapy behavioral interventions are grounded in evidence-based practice. Research studies have consistently demonstrated the effectiveness of these interventions in improving behavior, enhancing functional abilities, and promoting overall well-being. These studies provide empirical evidence that supports the use of specific behavioral interventions, such as positive reinforcement, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and environmental adaptation, in addressing behavioral issues across various populations and contexts.
Integration of best practice guidelines
Occupational therapists stay up-to-date with best practice guidelines in order to provide the most effective interventions in behavioral therapy. Best practice guidelines are developed based on the synthesis of research evidence, clinical expertise, and client preferences. By integrating these guidelines into their practice, occupational therapists ensure that their interventions are informed by the latest research, promote optimal outcomes, and adhere to ethical standards.
Role of Occupational Therapists in Implementing Behavioral Interventions
Evaluation and diagnosis
Occupational therapists play a pivotal role in evaluating and diagnosing behavioral issues within the scope of occupational therapy practice. Through comprehensive assessments, therapists collect information regarding the individual’s behavior, functional abilities, and environmental factors impacting behavior. Based on this evaluation, occupational therapists develop a holistic understanding of the individual’s needs, diagnose relevant behavioral issues, and establish a foundation for treatment planning.
Creating and implementing treatment plans
Occupational therapists are responsible for creating individualized treatment plans that outline specific behavioral interventions to address the identified issues. These treatment plans are based on collaborating with the individual and considering their unique needs, goals, and environmental context. Occupational therapists then implement the interventions in a structured and consistent manner, providing ongoing support, guidance, and feedback to facilitate behavior change and achieve desired outcomes.
Teaching and training individuals and caregivers
In addition to implementing interventions, occupational therapists also play a crucial role in teaching and training individuals and their caregivers in regards to behavioral management strategies. They educate individuals and their support network on the purpose, techniques, and goals of the behavioral interventions. Occupational therapists provide guidance on how to incorporate these interventions into daily routines, promote consistency, and reinforce functional behaviors. By empowering individuals and caregivers with the necessary knowledge and skills, occupational therapists support independence and long-term success in behavioral management.

Collaboration with Multidisciplinary Team in Occupational Therapy Behavioral Interventions
Working with doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals
Occupational therapists collaborate with a multidisciplinary team to ensure comprehensive care for individuals receiving occupational therapy behavioral interventions. This collaboration involves working closely with doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to share information, coordinate treatment plans, and provide holistic support. By collaborating with the broader healthcare team, occupational therapists contribute to a coordinated and integrated approach to behavioral management, ultimately enhancing the overall well-being and outcomes for individuals.
Coordinating care with other therapists and specialists
Occupational therapy often works in conjunction with other therapists and specialists to address the specific needs of individuals. For example, when addressing behavioral issues related to mental health, occupational therapists may collaborate with psychologists or psychiatrists to provide a holistic and multidimensional approach. This coordination ensures that individuals receive comprehensive care that addresses all aspects of their behavioral challenges and optimizes their potential for positive outcomes.
Challenges and Considerations in Occupational Therapy Behavioral Interventions
Adherence and motivation
One of the challenges in occupational therapy behavioral interventions is ensuring adherence and maintaining motivation throughout the therapeutic process. Behavioral change requires effort and consistency, which can be challenging for individuals facing behavioral issues. Occupational therapists use various strategies, such as goal setting, positive reinforcement, and ongoing support, to enhance motivation and encourage individuals to persevere even when faced with setbacks or difficulties.
Cultural and socioeconomic factors
Addressing behavioral issues in occupational therapy requires consideration of cultural and socioeconomic factors that may influence an individual’s beliefs, values, and access to resources. Occupational therapists must be culturally sensitive and aware of any potential barriers or biases that may affect the effectiveness of interventions. By understanding the individual’s cultural context and socioeconomic circumstances, therapists can tailor interventions to ensure they are relevant, feasible, and respectful of the person’s cultural background.
Ethical considerations
Occupational therapy behavioral interventions raise ethical considerations, particularly regarding the autonomy and rights of the individual. Occupational therapists must ensure that interventions are implemented with the informed consent of the individual, respecting their right to make decisions about their own care. Additionally, therapists must uphold ethical standards and consider potential risks and benefits when selecting and implementing particular interventions. By practicing ethical decision-making and maintaining open communication, occupational therapists can ensure the well-being and dignity of the individuals they serve.
In conclusion, occupational therapy behavioral interventions play a crucial role in addressing a wide range of behavioral issues across various populations. By employing strategies such as positive reinforcement, environmental adaptation, and cognitive-behavioral therapy, occupational therapists help individuals improve their quality of life, increase independence and productivity, and enhance physical and mental well-being. Through collaborative goal setting, individualized care plans, and ongoing evaluation, occupational therapy behavioral interventions promote person-centered care and tailored approaches that maximize outcomes. Moreover, the integration of evidence-based practice and collaboration with multidisciplinary teams ensure the delivery of comprehensive care. However, challenges such as adherence and motivation, cultural and socioeconomic factors, and ethical considerations must also be navigated to ensure ethical and effective occupational therapy behavioral interventions.