If you’re an educator looking for a tool to enhance student success, then the “Improving Student Success: School-Based Occupational Therapy Screening Form” might just be the solution you’re searching for. This innovative screening form, designed specifically for school-based occupational therapy, aims to identify and address any barriers that may be hindering a student’s academic and social performance. By targeting and addressing these barriers early on, educators and therapists can work together to create a supportive and inclusive learning environment, ultimately improving student success.
Overview
School-based occupational therapy (OT) is a specialized service designed to support students’ ability to participate in the educational environment. The purpose of school-based OT is to promote students’ functional capabilities through the use of targeted interventions and strategies. Early intervention is crucial in ensuring that students’ developmental needs are addressed promptly and effectively. One important tool that plays a vital role in identifying students’ needs is the screening form. Screening forms are comprehensive assessment tools that highlight areas of strength and areas that may require further support, allowing occupational therapists to develop individualized intervention plans.
Definition and Purpose of School-Based Occupational Therapy
School-based occupational therapy is a specialized service provided to students in an educational setting to enhance their participation and engagement in daily activities. Occupational therapists play a significant role in helping students develop the skills and abilities necessary for academic success and independent functioning. The ultimate goal of school-based OT is to support students in achieving their full potential and promoting their overall well-being.
The purpose of school-based OT is to address the unique challenges faced by students in their learning environment. Occupational therapists work collaboratively with teachers, parents, and other professionals to identify and address specific areas of need. This may include physical development, fine motor skills, visual motor skills, sensory processing, self-help skills, and social-emotional skills. By targeting these areas, school-based OT aims to enhance students’ functional performance and academic success.
Importance of Early Intervention for Students
Early intervention is crucial in any setting, including the educational environment, as it allows professionals to identify potential developmental delays or challenges that may hinder a student’s progress. In the context of school-based OT, early intervention is essential in addressing the specific needs of students and implementing appropriate strategies to support their growth.
By intervening early, occupational therapists can prevent potential difficulties from escalating and becoming more challenging to address. Early intervention also maximizes the impact of therapeutic interventions, as developmental issues can be addressed before they have a significant impact on academic performance and overall well-being. By identifying areas of concern early on, school-based OT can help set students on a path to success, laying a strong foundation for future learning and development.
Role of Screening Forms in Identifying Students’ Needs
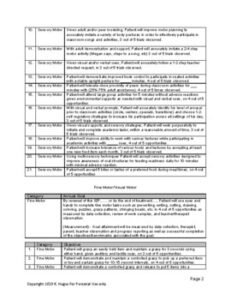
Screening forms are valuable tools used by occupational therapists to identify students’ strengths and areas that may require further support. These forms consist of various sections that assess different aspects of a student’s development. The information gathered from these assessments helps the occupational therapist gain a comprehensive understanding of each student’s needs, enabling them to tailor their interventions effectively.
The screening form covers critical areas such as physical development, fine motor skills, visual motor skills, sensory processing, self-help skills, and social-emotional skills. By evaluating these domains, occupational therapists can identify areas of strength and areas that may require intervention. The information obtained from the screening forms guides the development of individualized intervention plans, ensuring that the support provided aligns with each student’s unique needs.
Components of the Screening Form
The screening form consists of various components that assess different areas of a student’s development. These components aim to provide a comprehensive evaluation of functional capabilities and highlight potential areas of concern. Let’s explore each component in detail.
Physical Development
The physical development component of the screening form assesses gross motor skills, balance and coordination, as well as strength and endurance. Gross motor skills refer to the ability to perform activities that involve the large muscles of the body, such as running, jumping, and throwing. Occupational therapists evaluate a student’s gross motor skills to identify any limitations or delays that may impact their ability to participate fully in physical activities.
Balance and coordination play a crucial role in a student’s overall motor development. The screening form includes an evaluation of these skills to determine if there are any underlying deficits that may affect the student’s ability to perform daily activities or engage in classroom tasks.
Strength and endurance are also assessed as they directly impact a student’s ability to sustain activities over time. Occupational therapists evaluate the strength and endurance levels of students to identify any areas that may require additional support or intervention.
Fine Motor Skills
The fine motor skills component of the screening form focuses on the student’s ability to perform tasks that require precise hand and finger movements. Handwriting is a fundamental fine motor skill that is assessed to determine a student’s proficiency in writing legibly and efficiently.
Manipulative skills, such as the ability to manipulate small objects or use tools, are also evaluated. These skills are essential for activities such as buttoning clothes, using scissors, or manipulating puzzle pieces. By assessing these skills, occupational therapists can identify any areas of weakness or difficulty that may impede a student’s performance in academic or daily activities.
Visual Motor Skills
Visual motor skills refer to the ability to coordinate visual information with motor movements. These skills are crucial for tasks such as copying from the board, tracking words while reading, or completing puzzles. The screening form includes an evaluation of visual motor skills to determine if there are any underlying challenges that may affect a student’s ability to visually process and respond to information.
Hand-eye coordination, another aspect of visual motor skills, is also assessed. This skill requires the ability to coordinate hand movements with visual information. Occupational therapists evaluate hand-eye coordination to identify any difficulties that may hinder a student’s participation in activities that require precise motor control.
Sensory Processing
Sensory processing refers to how the brain receives and interprets sensory information from the environment. The screening form includes an assessment of sensory processing to determine a student’s sensory sensitivity, as well as their sensory seeking or avoiding behaviors.
Sensory sensitivity refers to a student’s reaction to sensory stimuli, such as noises, lights, or textures. Occupational therapists evaluate sensory sensitivity to identify any sensitivities that may affect a student’s ability to focus or engage in classroom activities.
Sensory seeking or avoiding behaviors assess the student’s preferences and reactions to sensory input. Some students may seek certain types of sensory input, such as deep pressure or movement, while others may avoid sensory experiences altogether. By understanding a student’s sensory preferences, occupational therapists can design interventions that support their sensory needs and promote optimal engagement in daily activities.
Self-Help Skills
Self-help skills are essential for a student’s independence and ability to care for themselves. The screening form assesses activities of daily living, such as dressing, eating, and personal hygiene, to identify any areas that may require intervention.
Personal hygiene evaluation focuses on a student’s ability to perform self-care tasks independently, including brushing teeth, washing hands, or grooming. Occupational therapists evaluate personal hygiene to determine if there are any difficulties that may impact a student’s overall well-being or social interactions.
Organizational skills, another important aspect of self-help skills, are also assessed. These skills include the ability to organize belongings, manage time, and follow routines. By evaluating organizational skills, occupational therapists can identify any areas that may require additional support and develop interventions that promote independence and success.
Social-Emotional Skills
Social-emotional skills encompass a wide range of abilities, including emotional regulation, peer interaction, and coping skills. The screening form assesses each of these domains to understand a student’s social and emotional functioning.
Emotional regulation evaluation focuses on a student’s ability to regulate their emotions in various situations. This includes managing frustration, staying calm, and expressing emotions appropriately. Occupational therapists assess emotional regulation to identify any difficulties that may impact a student’s ability to engage in classroom activities or maintain positive relationships.
Peer interaction assessment aims to evaluate a student’s ability to interact and communicate effectively with their peers. This includes initiating and maintaining conversations, sharing, and taking turns. Occupational therapists assess peer interaction to determine if there are any challenges that may affect a student’s social integration and overall well-being.
Coping skills evaluation focuses on a student’s ability to manage stress and adapt to new or challenging situations. This includes problem-solving, resilience, and self-regulation. By evaluating coping skills, occupational therapists can identify areas that may require additional support and develop strategies to help students effectively manage stressors and navigate daily challenges.
Screening Process
The screening process involves several steps that allow occupational therapists to gather relevant information, evaluate results, and develop individualized intervention plans. Let’s explore each step in detail.
Administering the Screening Form
The first step in the screening process is to administer the screening form to students. Depending on the school’s policies and resources, this may be done individually or in a group setting. Occupational therapists follow established guidelines and protocols to ensure consistent administration of the screening form, allowing for reliable and valid results.
During the screening, occupational therapists observe and interact with students to gather additional information relevant to each assessment component. This may include informal observations of the student’s performance during various tasks, conversations with the student, and collaboration with teachers or other educational professionals.
Evaluating the Results
After the screening form is administered, the occupational therapist carefully evaluates the collected information to gain a comprehensive understanding of each student’s strengths and areas of concern. The information is analyzed, and patterns or trends are identified to guide the development of appropriate interventions.
Occupational therapists use their professional expertise to interpret the results, taking into consideration developmental norms and standards. This allows them to determine if a student’s performance falls within the expected range or if additional support or intervention is necessary.
Identifying Areas of Concern and Strengths
Based on the evaluation of the screening form results, occupational therapists identify specific areas of concern and strengths for each student. Areas of concern may include deficits in fine motor skills, sensory processing challenges, or difficulties with emotional regulation. Identifying these areas allows occupational therapists to address them directly and provide targeted interventions.
Additionally, the screening form also highlights areas of strength, such as well-developed gross motor skills or effective coping strategies. Recognizing these strengths allows occupational therapists to build upon them and incorporate them into the intervention plans, promoting students’ overall growth and success.
Developing Individualized Intervention Plans
Once areas of concern and strengths are identified, occupational therapists develop individualized intervention plans tailored to each student’s unique needs. These plans outline specific strategies, techniques, and activities that will be used to address areas of concern and support students’ development.
Intervention plans may include direct therapeutic interventions, classroom modifications, collaboration with teachers and other professionals, and recommendations for home-based activities. The goal of these plans is to provide students with the necessary support to maximize their potential, improve their functional capabilities, and foster their overall well-being.
Benefits of the Screening Form
The screening form serves as a valuable tool in optimizing student success and academic performance. Let’s explore some of the key benefits that the screening form offers.
Early Identification of Students’ Needs
One of the primary benefits of the screening form is its ability to identify students’ needs at an early stage. By assessing various areas of development, occupational therapists can identify potential challenges or delays before they significantly impact a student’s functioning. This early identification allows for timely intervention and support, preventing difficulties from escalating and addressing them proactively.
Tailoring Interventions to Meet Specific Needs
The screening form provides occupational therapists with a comprehensive understanding of each student’s strengths and areas of concern. This information is crucial in developing individualized intervention plans that specifically target areas requiring support. By tailoring interventions to meet specific needs, occupational therapists can provide students with the most effective strategies, techniques, and resources, maximizing the potential for growth and success.
Improving Student Success and Academic Performance
The ultimate goal of school-based occupational therapy is to support students’ functional capabilities and promote their overall well-being. By using the screening form, occupational therapists can identify and address areas of need, ensuring that students receive the necessary support to excel academically and engage fully in their daily activities. By optimizing students’ skills and abilities, school-based OT helps pave the way for success, enhancing their educational experience and fostering their long-term development.
In conclusion, the school-based occupational therapy screening form is a valuable assessment tool that plays a vital role in identifying student needs, guiding intervention, and supporting students’ overall growth and success. Through its comprehensive evaluation of physical development, fine motor skills, visual motor skills, sensory processing, self-help skills, and social-emotional skills, the screening form enables occupational therapists to develop individualized intervention plans that address specific areas of concern and promote optimal functioning. By intervening early, tailoring interventions to meet specific needs, and improving student success and academic performance, the screening form serves as an invaluable resource in the field of school-based occupational therapy.